
To find the right stocks to invest in, it's not enough to simply start looking for specific companies that are doing well. Reason: even a good company in an underperforming industry, or one facing adverse economic and technological challenges, will find it tough to sustain its out-performance.
Which is why it is important to first identify strong performing or otherwise favorably placed industries, and then look for leading companies in those sectors to invest in...
The importance of industry analysis is slowly dawning on the Indian investor as never before.
Previously, investors purchased shares of companies without concerning themselves about the industry it operated in.
And they could get away with it three decades ago. This was because India was a sellers' market at that time and products produced were certain to be sold, often at a premium.
Those happy days are long over. Now, there is intense competition.
Consumers have now become quality, cost and fashion conscious.
Foreign goods are easily available and Indian goods have to compete with these. There are great technological advances and 'state of the art' equipment becomes obsolete in a few years, if not months.
Click on NEXT to read more...

In the same way, technological advances in one industry can affect another industry. The jute industry went into decline when alternate and cheaper packing materials began to be used.
The popularity of cotton clothes in the West affected the manmade (synthetic) textile industry.
An investor must therefore examine the industry in which a company operates because this can have a tremendous effect on its results, and even its existence.
A company's management may be superior, its balance sheet strong and its reputation enviable.
However, the company may not have diversified and the industry within which it operates may be in a depression.
This can result in a tremendous decline in revenues and even threaten the viability of the company.
Cycle
The first step in industry analysis is to determine the cycle it is in, or the stage of maturity of the industry.
The life cycle of an industry can be illustrated in an inverted 'S' curve.
Click on NEXT to read more...

The entrepreneurial or nascent stage
At the first stage, the industry is new and it can take some time for it to properly establish itself.
In these early days, it may actually make losses. At this time there may also not be many companies in the industry.
It must be noted that the first 5 to 10 years are the most critical period. At this time, companies have the greatest chance of failing. It takes time to establish companies and new products.
There may be losses and the need for large injections of capital. If a company or an industry is not nurtured or husbanded at this stage, it can collapse.
A good journalist I know began a business magazine. His intention was to start a magazine edited by journalists without interference from industrial magnates or politicians. It was an exceptionally readable magazine.
However, it did not have the finance needed in those critical initial years to keep it afloat and had to fold up. Had it, at that time, had the finance it needed it may have survived and thrived.
In short, at this stage investors take a high risk in the hope of great reward should the product succeed.
The industry cycle:
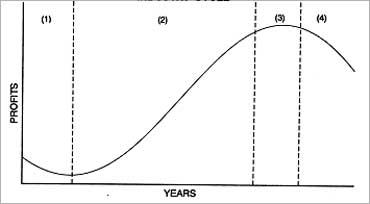

The expansion or growth stage
Once the industry has established itself it enters a growth stage. As the industry grows, many new companies enter the industry.
At this stage, investors can get high reward at low risk since demand outstrips supply.
In 2000, a good example was the Indian software industry. In 2003, the BPO industry is arguably in the growth stage.
The mobile phone industry is also in the growth stage - with newer models and newer entrants.
The growth stage also witnesses product improvements by companies that have survived the first stage.
In fact, such companies are often able to even lower their prices. Investors are more keen to invest at this time as companies would have demonstrated their ability to survive.
Click on NEXT to read more...

The stabilisation or maturity stage
After the halycon days of growth, an industry matures and stabilizes. Rewards are low and so too is the risk.
Growth is moderate. Though sales may increase, they do so at a slower rate than before.
Products are more standardised and less innovative and there are several competitors.
The refrigerator industry in India is a mature industry. Growth is slow.
It is for the time seeing safe. Investors can invest in these industries for comfort and average returns.
They must be aware though that should there be a downturn in the economy and a fall in consumer demand, growth and returns can be negative.
Click on NEXT to read more...

The decline or sunset stage
Finally, the industry declines. This occurs when its products are no longer popular.
This may be on account of several factors such as a change in social habits (the film and video industry, for example, has suffered on account of cable and satellite television), changes in laws, and increase in prices.
The risk at this time is high but the returns are low, even negative.
The various stages can be likened to the four stages in the life cycle of a human being - childhood, adulthood, middle age and old age.
Investors should begin to purchase shares when an industry is at the end of the entrepreneurial or nascent stage and during its growth stage, and should begin to disinvest when at its mature stage.
[Excerpt from Fundamental Analysis for Investors by Raghu Palat]. Published by Vision Books
(C) All rights reserved